Six Sigma
An Overview of Six Sigma Methodology


© The Quality Web, authored by Frank E. Armstrong, Making Sense Chronicles - 2003 - 2016
Overview of Six Sigma - DMAIC
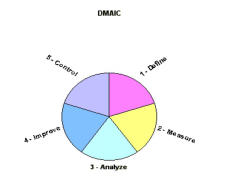
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for the 5 major steps within the Six Sigma program. They are: • D - Define • M - Measure • A - Analyze • I - Improve • C - Control DMAIC is a structured, disciplined and aggressive approach to process improvement that consists of the above five phases. Each phase is linked logically to the previous phase, and to the next phase at the same time. The purpose of this rigorous methodology is to achieve the overall goal of Six Sigma, which is 3.4 defects per million parts, or opportunities. We will discuss each step in detail, and then hopefully acquaint you with what tools to use for which phase, how and when. PHASE ONE - DEFINE In this phase, the project's purpose and scope are defined. Customer information and background information on the process is collected. The output of this phase is: 1. A clear statement of the intended improvement. 2. A high-level map of the process (SIPOC - defined further later). 3. A list of what is important to the customer (Voice of the customer). PHASE TWO - MEASURE The goal of the Measure phase is to focus the improvement effort by gathering information on the current situation. The output of Measure is: 1. Baseline data on current process performance. 2. Data that pinpoints problem location or occurrence. 3. A more focused problem statement. PHASE THREE - ANALYZE The goal of the Analyze phase is to identify root cause(s) and confirm those with data. The output is a theory that has been tested and confirmed. The verified cause(s) will form the basis for solutions in the next phase. PHASE FOUR - IMPROVE The goal of the Improve phase is to do trials and implement solutions that address the identified root cause(s). The output is planned, tested actions that should eliminate or reduce the impact of the identified root cause(s). A plan is also created as to how the results will be evaluated in the next phase. PHASE FIVE - CONTROL The goal of the Control phase is to evaluate the solutions and the plan, maintain the gains accomplished by standardizing the process, and outline steps for on-going improvements including opportunities for replication. It is also important to consider if this improvement affects similar lines of production. The output is: 1. Before and after analysis. 2. A monitoring system. 3. Completed documentation of results, learnings, and recommendations.















Six Sigma
An Overview of Six Sigma Methodology


© The Quality Web, authored by Frank E. Armstrong, Making Sense
Chronicles - 2003 - 2016
Overview of Six Sigma - DMAIC
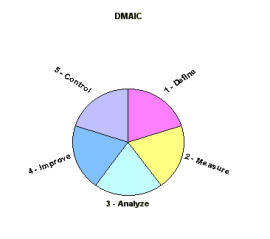
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for the 5 major steps within the Six Sigma program. They are: • D - Define • M - Measure • A - Analyze • I - Improve • C - Control DMAIC is a structured, disciplined and aggressive approach to process improvement that consists of the above five phases. Each phase is linked logically to the previous phase, and to the next phase at the same time. The purpose of this rigorous methodology is to achieve the overall goal of Six Sigma, which is 3.4 defects per million parts, or opportunities. We will discuss each step in detail, and then hopefully acquaint you with what tools to use for which phase, how and when. PHASE ONE - DEFINE In this phase, the project's purpose and scope are defined. Customer information and background information on the process is collected. The output of this phase is: 1. A clear statement of the intended improvement. 2. A high-level map of the process (SIPOC - defined further later). 3. A list of what is important to the customer (Voice of the customer). PHASE TWO - MEASURE The goal of the Measure phase is to focus the improvement effort by gathering information on the current situation. The output of Measure is: 1. Baseline data on current process performance. 2. Data that pinpoints problem location or occurrence. 3. A more focused problem statement. PHASE THREE - ANALYZE The goal of the Analyze phase is to identify root cause(s) and confirm those with data. The output is a theory that has been tested and confirmed. The verified cause(s) will form the basis for solutions in the next phase. PHASE FOUR - IMPROVE The goal of the Improve phase is to do trials and implement solutions that address the identified root cause(s). The output is planned, tested actions that should eliminate or reduce the impact of the identified root cause(s). A plan is also created as to how the results will be evaluated in the next phase. PHASE FIVE - CONTROL The goal of the Control phase is to evaluate the solutions and the plan, maintain the gains accomplished by standardizing the process, and outline steps for on-going improvements including opportunities for replication. It is also important to consider if this improvement affects similar lines of production. The output is: 1. Before and after analysis. 2. A monitoring system. 3. Completed documentation of results, learnings, and recommendations.